 Using SHAZAM as a Calculator
Using SHAZAM as a Calculator
- Arithmetic
- Calculating a Sample Mean and Variance
- Calculating a Mean and Variance for 2 Different Samples
- Calculating the Mean Absolute Deviation
- Calculating Factorials and Combinations
 [SHAZAM Guide home]
[SHAZAM Guide home]
Arithmetic
The GEN1 command can be used as a calculator.
For example, the command below computes and prints a sum of numbers:
GEN1 40+55+10 |
Results can be saved for use in subsequent calculations. This is illustrated in the next example.
GEN1 REV=3000+1326 GEN1 COST=48+89.5+1200 GEN1 PROFIT=REV-COST PRINT REV COST PROFIT STOP |
Calculating a Sample Mean and Variance
The next commands calculate the mean, variance and standard deviation for a sample of 6 observations. Note that the calculation for the sample variance uses a divisor of 5.
SAMPLE 1 6 READ X / BYVAR 23 43 26 43 13 22 STAT X STOP |
Calculating a Mean and Variance for 2 Different Samples
Consider 2 samples of observations. The first sample has 6 observations and the second sample has 9 observations. The commands below show how to calculate a mean and variance for each sample.
SAMPLE 1 6 READ X / BYVAR 23 43 26 43 13 22 STAT X * The second sample has 9 observations SAMPLE 1 9 * Be sure to give the second variable a different name than X READ Y / BYVAR 38 58 23 678 432 23 52 2 55 STAT Y STOP |
Calculating the Mean Absolute Deviation
SAMPLE 1 6 READ X / BYVAR 23 43 26 43 13 22 STAT X / MEAN=M GENR AD=ABS(X-M) STAT AD STOP |
The SHAZAM output follows.
|
The mean absolute deviation is listed as the MEAN in the
output from the final STAT command.
The results show that the mean absolute deviation is 9.7778.
Calculating Factorials and Combinations
A result from calculus is that for an integer n:
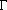 (n) =
(n
(n) =
(n - 1)!
where 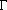 (n) is the gamma function.
With the
(n) is the gamma function.
With the GENR or GEN1 commands
the LGAM function calculates the log of the gamma
function. The anti-log of this function can be used to compute
factorials. For example, the number 5!
is calculated with the following SHAZAM commands.
SAMPLE 1 1 GEN1 N=5 GEN1 FAC=EXP(LGAM(N+1)) PRINT FAC STOP |
Now consider the problem of calculating the number of combinations of k objects chosen from n. The formula, known as the "binomial coefficient", is:
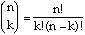
An example is shown with the next SHAZAM commands.
SAMPLE 1 1 GEN1 N=6 GEN1 K=3 GEN1 C=EXP(LGAM(N+1)-LGAM(K+1)-LGAM(N-K+1)) PRINT C STOP |
The SHAZAM output follows.
|
The result shows that the total number of combinations of 3 objects chosen from 6 is 20.
 [SHAZAM Guide home]
[SHAZAM Guide home]